Hyperspectral Imaging
Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) is an advanced method for capturing spectral information from a sample. Unlike conventional imaging, which only registers three spectral frequencies (red, green, and blue), HSI collects a wide range of spectral frequencies across the electromagnetic spectrum. This allows for more precise analysis and identification of specific features that are not visible in standard imaging.
How Hyperspectral Imaging Works
To perform hyperspectral imaging, light from a source emitting the desired spectral range is directed onto the sample. This light may be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed by the sample depending on sample surface chemical properties. Each molecule absorbs or reflects light at specific wavelengths based on its physical and chemical characteristics. For instance, plants reflect green light and absorb red and blue light more, but hyperspectral data provides additional information about specific absorption and reflection features across multiple wavelengths. A hyperspectral device uses specialized sensors that break down the reflected or transmitted light from the scene into multiple frequencies. At this stage, the electromagnetic spectrum is divided into hundreds of narrow bands across various wavelengths (from ultraviolet to near-infrared). The hyperspectral sensor collects spectral data for each pixel in the image. In other words, a full spectrum is captured for each pixel. These data are stored as a three-dimensional cube, where two dimensions represent spatial location, and the third dimension represents the spectrum. Each band in this data cube corresponds to a specific wavelength. The analysis of this data is then carried out in line with the intended objectives.
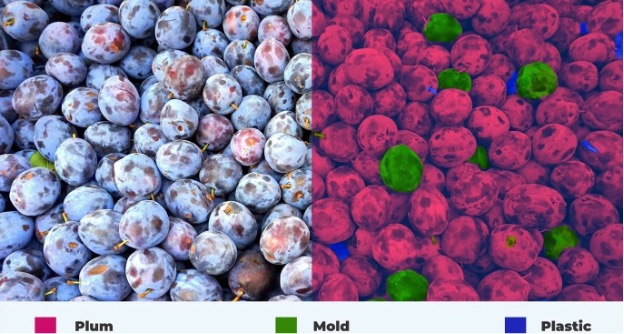
Non-Destructive Measurement in Quality Control
Non-destructive measurement in food quality control refers to a set of methods and techniques aimed at evaluating and examining the characteristics of a product without damaging it. This type of measurement is essential in situations where the sample cannot be damaged or when there are associated costs. These methods use physical technologies based on sound waves and electromagnetic waves, utilizing sensors to evaluate the desired features in the sample. Non-destructive measurement may sometimes result in measurement errors, especially when measuring the concentration of materials, but in many cases, it remains acceptable and is often fast and efficient. These methods are particularly useful in production lines for online monitoring. Overall, non-destructive measurement in quality control helps improve production standards, reduce waste, and increase customer satisfaction.
Combining hyperspectral imaging with various modeling techniques, such as least squares regression, can be used to predict desired features based on a trained model. The integration of image processing techniques, chemometrics, and artificial neural networks provides various capabilities for non-destructive measurement of food products.
Applications in the Food Industry
Since hyperspectral imaging provides the spectrum for each defined pixel in the image for analysis, it enables more accurate image segmentation compared to conventional and multispectral imaging. Some of the applications proposed for this technique include:
- Examining characteristics like firmness and blemishes in fruits and vegetables, such as apples and mushrooms
- Analyzing chemical properties, color, and texture of seafood products like fish fillets
- Analyzing color, texture, fat quality, microbial contamination, and some chemical properties in meat cuts
- More accurate segmentation of components, in cases where visible imaging does not provide sufficient contrast.
However, research continues to develop applications for this technique, especially for online monitoring of products during production. The following capabilities for hyperspectral imaging have been proposed:
- Determining the central temperature and moisture content of meat products during the cooking process
- Determining moisture content during the drying process
- Estimating the concentration of ions such as sodium in processed products
- Monitoring changes in chemical composition during cooking processes
- Detecting fraud in valuable products such as spices and tea
- Classifying and categorizing products
For further details, refer to articles on image processing applications in the food industry and artificial intelligence in the future of food.

