Introduction to Food Colors in the Food Industry
Color is the first stimulus the human eye perceives when observing a food product. Before taste or texture is sensed, color determines whether a product looks appealing, fresh, or trustworthy. For this reason, food coloring is considered one of the primary tools in the food industry and marketing.
In modern production, colors are applied not only for visual appeal but also to stabilize product quality and standardize their appearance. Innovative brands and companies such as the Grownida Innovation Center strive to provide natural and sustainable food colors that ensure both aesthetic appeal and consumer health.
History of Food Color Use and Its Impact on Sales
The use of color in food dates back to ancient times. Egyptians and Romans used natural colors like saffron, beetroot, and vegetables to enhance the visual appeal of food. With the industrial revolution in the 19th century and the rise of mass production, synthetic food colors emerged, enabling uniform and stable coloring.
As public awareness of health increased, some countries limited the use of synthetic colors. International organizations such as EFSA and FDA have set standards for approved food colors. Studies show that 85% of food purchase decisions depend on a product’s appearance, with color playing a key role.

The Impact of Food Colors on Consumer Perception and Buying Behavior
Colors are closely linked to human emotions. Red conveys excitement and energy, yellow evokes happiness and stimulates appetite, and green represents health and freshness.
- In Beverages: Bright and transparent colors suggest freshness and coolness, such as lemon yellow or orange.
- In Confectionery: Warm colors like pink and purple stimulate appetite.
This explains why brands and research centers like Grownida place special emphasis on developing natural and visually appealing colors for food and beverages.
Differences Between Natural and Synthetic Food Colors
Natural food colors are extracted from plant, animal, or mineral sources:
- Carmine from cochineal insects
- Chlorophyll from green leaves
- Beta-carotene from carrots
Synthetic food colors are chemically synthesized compounds with higher stability under light and heat, though there are health concerns for consumers. Brands like Grownida in Iran are working to offer highly stable natural colors as suitable alternatives to synthetic options.

Approved Food Colors in the Iranian Food Industry
The Iranian Food and Drug Administration has published a list of approved food colors aligned with European Union standards. These colors are used in beverages, dairy products, confectionery, sauces, and meat products. Some of the most commonly used include:
- Tartrazine (E102)
- Ponceau 4R (E124)
- Brilliant Blue FCF (E133)
- Carmine (E120)
- Beta-carotene (E160a)
These colors must meet stability and safety standards in addition to providing visual appeal.
Read more: What is Brilliant Blue food coloring?
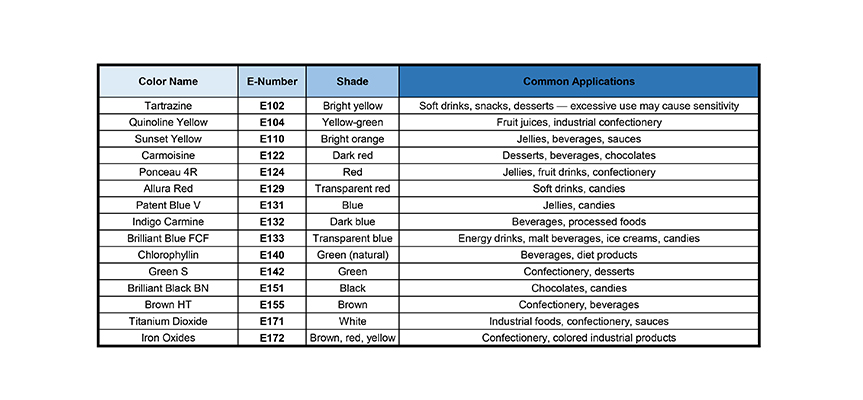
Complete Introduction to Some Widely Used Food Colors and Their E-Numbers
Here are 15 of the most consumed food colors worldwide, presented descriptively:
- Tartrazine (E102): Bright yellow, used in soft drinks, snacks, and desserts. Excessive consumption may cause sensitivity.
- Quinoline Yellow (E104): Yellow-green, used in fruit juices and industrial confectionery.
- Sunset Yellow (E110): Bright orange, commonly used in jelly, beverages, and sauces.
- Carmoisine (E122): Dark red, applied in desserts, beverages, and chocolates.
- Ponceau 4R (E124): Red, used in jelly, fruit drinks, and confectionery.
- Allura Red (E129): Transparent red, widely used in soft drinks and candies.
- Patent Blue V (E131): Blue, applied in jellies and candies.
- Indigo Carmine (E132): Dark blue, used in beverages and processed foods.
- Brilliant Blue FCF (E133): Transparent blue, found in energy drinks, malt beverages, ice creams, and candies.
- Chlorophyllin (E140): Green, natural color extracted from leaves, used in beverages and diet products.
- Green S (E142): Green, used in confectionery and desserts.
- Brilliant Black BN (E151): Black, applied in chocolates and candies.
- Brown HT (E155): Brown, commonly used in confectionery and beverages.
- Titanium Dioxide (E171): White, used in industrial foods, confectionery, and sauces.
- Iron Oxides (E172): Brown, red, and yellow, applied in confectionery and colored industrial products.
Challenges and Solutions in Maintaining Color Stability
One major challenge in the food industry is preserving color stability against light, heat, and pH changes. Many natural colors become unstable in acidic environments or at high temperatures.
Food color stabilizers play a key role by increasing resistance through natural and chemical compounds. Modern technologies, such as polyphenols or plant proteins, help maintain natural colors in stable products.
The Future of Food Colors
New-generation consumers prefer natural colors. By 2030, it is predicted that over 60% of the global market will shift toward natural and sustainable colors. Iran, with native plant sources like saffron and green herbs, has the potential to produce high-quality natural colors.
Conclusion
Food colors play a vital role in consumer experience, marketing, and health. Understanding the most consumed food colors worldwide, the differences between natural and synthetic colors, and considering stability and safety illuminates the path for food industry development. Brands and centers like the Grownida Innovation Center are shaping a healthier future for food coloring through innovation and research.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is food coloring and how is it made?
It is a compound used to alter or stabilize the color of food products.
Why is food coloring used in the food industry?
Food colors enhance the visual appeal, create visual harmony, stimulate appetite, and convey a sense of freshness and quality to the consumer.
Which are the most consumed food colors in the world?
Tartrazine (E102), Sunset Yellow (E110), Carmoisine (E122), Brilliant Blue FCF (E133), Chlorophyllin (E140), and Titanium Dioxide (E171) are among the most widely used.
Which food colors are most commonly used in beverages?
Yellow and orange colors such as Tartrazine and Sunset Yellow are most frequently used in carbonated drinks and juices due to their visual appeal and stability in acidic environments.
Are natural food colors better than synthetic ones?
Natural colors are generally safer and healthier, offering antioxidant properties along with visual appeal; however, their stability may be lower, and they can change under high temperatures or extreme pH conditions.

