The Role of Biotin in Hair Growth
In recent years, the variety of products designed to support hair growth and thickness has significantly increased. Most of these products contain multiple ingredients, with biotin (vitamin B7) being a common component. Biotin plays a crucial role in improving hair growth, particularly in individuals experiencing hair thinning or loss due to biotin deficiency. Other vitamin deficiencies may also impact hair health. Whether taken as a supplement or used in shampoos, biotin is widely promoted for its potential benefits in supporting hair growth.
The Impact of Biotin on Hair Health
Biotin provides several benefits to the body, primarily aiding metabolism and energy production. It is essential for keratin production, a structural protein that forms hair, skin, and nails. Many foods naturally contain biotin, making deficiency rare among individuals with a balanced diet. However, insufficient biotin levels can lead to skin rashes, brittle nails, and hair thinning or loss. Consequently, biotin-containing supplements and hair products are marketed to enhance hair growth, strength, and thickness.
A study involving individuals with self-perceived hair thinning examined the effects of a biotin-containing hair growth supplement over six months. Participants receiving the supplement reported significant increases in hair volume, scalp coverage, and strand thickness compared to those in the placebo group. However, as these supplements also included essential hair growth nutrients like zinc and iron, it remains unclear whether the observed effects were solely attributable to biotin.

Can Biotin Prevent Hair Loss?
While evidence supporting biotin’s role in hair growth remains limited, its potential for preventing hair loss is slightly better documented. Research suggests that biotin supplements help prevent hair loss and improve hair growth in individuals with biotin deficiency. One study found a correlation between hair loss and insufficient biotin levels, with 38% of female participants reporting hair loss exhibiting biotin deficiency. Among these participants, 11% had inflammatory bowel disease or a history of using medications such as antibiotics, which can affect biotin absorption.
Other Causes of Hair Loss
Apart from biotin deficiency, various factors contribute to hair thinning and loss, including:
- Androgenic alopecia (female pattern baldness)
- Rapid weight loss
- Deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron, zinc, or protein
- Hormonal disorders such as thyroid dysfunction
Given the multiple causes of hair loss, taking biotin supplements without identifying the underlying reason may delay or hinder appropriate treatment. Even in cases of biotin deficiency, supplementation does not always guarantee prevention of hair loss. For example, a study on post-bariatric surgery patients with low biotin levels found mixed results: after three months of supplementation, five individuals reported significant hair loss reduction, fourteen noted mild improvement, and three saw no effect. These findings suggest that other factors may also influence hair health.
Daily Biotin Requirements and Dietary Sources
The Food and Nutrition Board at the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine establishes recommended dietary allowances (RDA) for essential nutrients. When sufficient data is unavailable to determine an RDA, an adequate intake (AI) level is established. For biotin, the AI is set at 30 micrograms per day for adults and 35 micrograms for lactating women. A well-balanced diet generally meets these needs, with U.S. residents estimated to consume between 35-70 micro g of biotin daily.
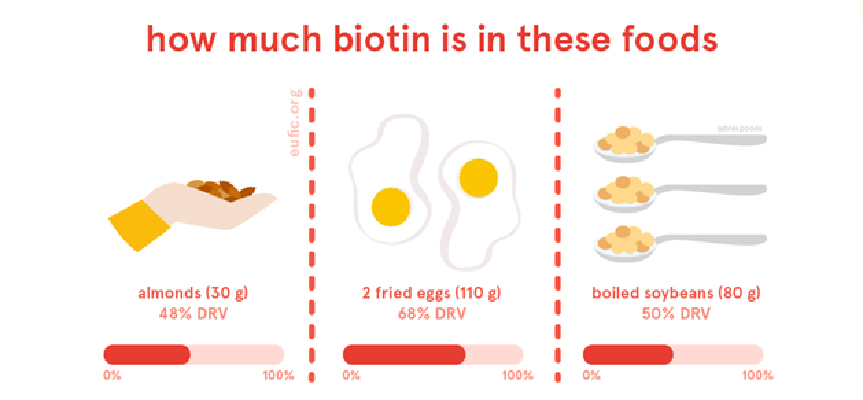
Top Biotin-Rich Foods
| Food Source | Biotin Content (micro g) | % Daily Value (DV) |
| Beef liver (85g) | 30.8 | 103% |
| Whole egg | 10 | 33% |
| Salmon (85g) | 5 | 17% |
| Hamburger (85g) | 3.8 | 13% |
| Sunflower seeds (33g) | 2.6 | 9% |
| Sweet potato (77g) | 2.4 | 8% |
| Almonds (36g) | 1.5 | 5% |
Eggs are an excellent biotin source, but consuming them raw reduces biotin availability due to avidin, a glycoprotein that binds to biotin and inhibits absorption. Cooking deactivates avidin, allowing biotin to be effectively absorbed. The FDA does not mandate biotin content labeling on food packaging unless biotin is added during processing.
Who Is at Risk of Biotin Deficiency?
Certain individuals are more susceptible to biotin deficiency, including:
- Biotinidase deficiency (BTD): A genetic disorder that impairs biotin recycling and utilization.
- Chronic alcohol consumption: Alcohol inhibits biotin absorption, leading to deficiency over time.
- Malnutrition: Insufficient dietary intake can reduce biotin levels.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis may disrupt biotin production by gut bacteria.
- Pregnant and lactating women: Increased biotin utilization and possible absorption issues can lead to lower levels.
- Individuals taking certain medications: Antiepileptic drugs and retinoids may interfere with biotin metabolism.
For individuals outside these risk groups, biotin supplementation or biotin-enriched hair products are unlikely to provide significant benefits.
Risks and Considerations
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin, making toxicity unlikely. However, excessive biotin intake may lead to mild side effects such as insomnia, excessive thirst, and increased urination. Additionally, high biotin levels can interfere with laboratory tests, including thyroid hormone, vitamin D, and cardiovascular health assessments, potentially leading to inaccurate results. Since biotin is frequently used in diagnostic tests due to its ability to bind to specific proteins, individuals taking biotin supplements should inform their healthcare providers.